Native Christians of the 7 islands off Bombay, the island of Salsette, Thana, Bassein (Vasai), Chaul, Dahanu, Palghar and surrounding areas
Introduction of The East Indians of Bombay
The East Indians are natives of
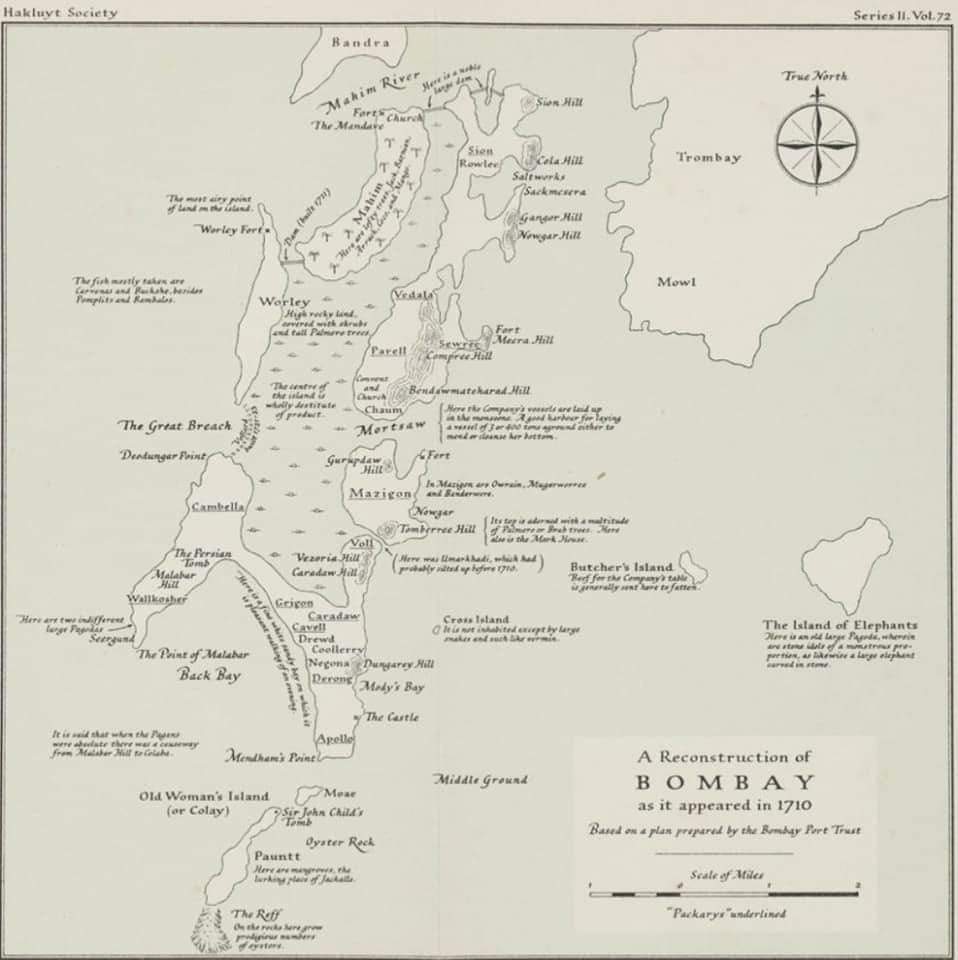
1) The seven islands off Bombay (Mahim, Worli, Parel, Mazagaon, Bombay (Mobai), Colaba, Old Woman’s Island),
2) The island of Salsette including the statelite islands of Jewe (Juhu) and the island of Versave (Versova), the island of Aldea Mar (Madh Island) and Aksa.
3) Bassein (Vasai)
4) Thana
5) And its surroundings
The East Indians are Christians since early Christian period.
Though It is commonly thought that the origin of Christianity in North Konkan (west coast of Maharshtra, India), was due to the proselytizing activities of the Portuguese in the 16th Century.
It was, St. Bartholomew, one of the twelve Apostles of Christ, who preached in North Konkan

In 1887 the various castes and communities came together to collectively take the name of “East Indians of Bombay” and come into the British legal system.
Refer to the 1927 Golden Jubilee Souvenir in the Archives section, there is an article on Why the name East Indian was adopted.
Very often people have taken the easiest way out by stating that the name “East Indian” relates to “East India Company”. Historically, there were British East India Company, French East India Company, Dutch East India Company and maybe others that came into India. We have to remember that the British East India Company lost favor of the British Crown after the Great Indian Revolt (Indian Mutiny) in 1857 and eventually dissolved in 1874. To expect that a community would take the name “East Indian” because of the British East India Company (after it lost favor with the British Crown) and make that as a presentation to Queen Victoria in 1887, is illogical and (at that time) would have been considered seditious.
Some People feel that East Indians of Bombay got jobs from the British East India Company. Bombay (the island) was indeed developing far faster than its surrounding islands. However, in the 1800 and even in the early 1900, a huge majority of East Indians had their own lands doing farming, animal husbandry and various other businesses.
east.indians.bombay@gmail.com
